- Which of the following
hardware devices is used to
connect networks together?
- HUB
- Router
- Firewall
- Any of the above
- None of the above
- Which of the following
hardware devices is used
to connect multiple
computers to a LAN?
- HUB
- Router
- Firewall
- Any of the above
- None of the above
- What is the speed of
an Ethernet LAN?
- 10 Mbps
- 100 Mbps
- 1 Gigabit
- Any of the above
- None of the above
- Peer-to-peer networks do not
require a dedicated server.
- True
- False
- All broadband Internet
connections employ a
fixed IP address.
- True
- False
- A broadband connection
can be used for:
- Internet connection.
- remote video monitoring.
- VoIP.
- security system monitoring.
- All of the above
- When two devices on a
network try to send data at
once, a collision occurs.
- True
- False
- Which of the following is
a protocol for automatically
obtaining an IP address
on a network?
- ARP
- DHCP
- Ping
- Telnet
- Stackable hubs are designed
to be linked together to
expand the network.
- True
- False
- A firewall is hardware/soft-
ware that protects a network
from external systems.
- a. True
- b. False
- A broadband connection
can be obtained from:
- cable.
- DSL.
- satellite.
- Any of the above
- All DSL lines provide the
identical bandwidth.
- True
- False
- A print server can be
used to connect a printer
to a network.
- True
- False
- Which of the following
UTP cable types offers the
highest data rate?
- Cat-3
- Cat-5
- Cat-6
- They are all the same.
- Which of the following
jacks are used to connect
computers to a network?
- RJ-11
- RJ-31X
- RJ-45
- Any of the above
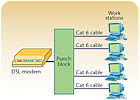
What’s Wrong with This?
Wally `Larman was asked to install a network connecting four computers and a DSL line for a residential client that currently had the DSL line connected directly to a single computer. Wally removed the DSL cable from the existing computer and connected the wires on a punch block, ran Cat-6 cables to each computer, and connected the cables as shown in this diagram. When he tried to test the system, he discovered that it did not work as intended. Can you see what Wally did wrong and what he must do to correct the problem?5-Minute Tech Quiz Answers
1. b – A router is used to connect multiple computer networks together.2. a – A HUB is a network device used to connect computers on a single LAN. To provide superior bandwidth, sharing a switch can be used in place of a HUB.
3. d – An Ethernet LAN can support any of these speeds depending upon the hardware and cabling used.
4. a
5. b – Most ISPs use DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). If you require a fixed IP address, you must specify that when ordering the line.
6. e
7. a
8. b
9. a – Stacking HUBs allows you to expand a network by adding a new HUB when all available ports on the existing HUB are occupied. This feature allows you to expand the network without discarding existing hardware.
10. a
11. d – Although a broadband connection can be obtained from any of these sources, the data rates will not always be the same. It is important that you verify the speed offered by your vendor of choice to ensure it meets your requirements.
12. b
13. a
14. c
15. c – RJ-11 jacks are used to connect telephones, RJ-31X for digital communicators and RJ-45 for data networks.